更新時(shí)間:2022-08-09 11:33:59 來(lái)源:動(dòng)力節(jié)點(diǎn) 瀏覽1864次
動(dòng)力節(jié)點(diǎn)小編通過(guò)編程示例來(lái)向大家解釋如何使用 Java Timer 類在 Java 中設(shè)置計(jì)時(shí)器:
下面給出的是 Java Timer 類支持的方法。
void cancel():該方法終止當(dāng)前或本次Timer,同時(shí)取消所有當(dāng)前調(diào)度的任務(wù)。
int purge():取消后,purge() 方法從隊(duì)列中移除所有取消的任務(wù)。
void schedule(TimerTask task, Date time):將要在指定時(shí)間執(zhí)行的任務(wù)排成一行。
void schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period):也將任務(wù)排成指定開始時(shí)間,然后重復(fù)執(zhí)行。
void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay):延遲后也會(huì)排隊(duì)執(zhí)行任務(wù)。
void schedule(TimerTask task, long delay, long period):它還排列任務(wù)以重復(fù)執(zhí)行,但它以指定的延遲開始。
void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period): 也將任務(wù)排成一行,以重復(fù)固定速率執(zhí)行,任務(wù)在指定時(shí)間開始。
void scheduleAtFixedRate(TimerTask task, long delay, long period):它還排列任務(wù)以重復(fù)但以固定速率執(zhí)行,并且任務(wù)以指定的延遲開始。
下面是一個(gè) Java Timer 示例,其中包括調(diào)度指定任務(wù)以以固定延遲重復(fù)執(zhí)行的功能,并且該任務(wù)具有一些指定的開始時(shí)間。
首先,我們聲明了一個(gè)擴(kuò)展 TimerTask 類的 Helper 類。在這個(gè) TimerTask 中,我們初始化了一個(gè)變量,用于檢查執(zhí)行的計(jì)數(shù)。
TimerTask 類的 run() 方法用于打印執(zhí)行完成的次數(shù)。在 main 方法中,我們使用了 schedule() 方法的“void schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)”變體來(lái)執(zhí)行 run() 方法任意多次。
我們明確需要停止執(zhí)行,否則 run() 方法將繼續(xù)執(zhí)行。
import java.util.Timer;
import java.util.TimerTask;
class Helper extends TimerTask {
public static int i = 1;
// TimerTask.run() method will be used to perform the action of the task
public void run() {
System.out.println("This is called " + i++ + " time");
}
}
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
// Helper class extends TimerTask
TimerTask task = new Helper();
/*
* Schedule() method calls for timer class.
* void schedule(TimerTask task, Date firstTime, long period)
*/
timer.schedule(task, 200, 5000);
}
}
輸出:
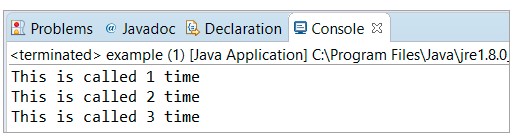
這是包含 cancel() 方法功能的 Java Timer 類的示例。眾所周知,cancel() 方法用于終止此 Timer 并丟棄任何計(jì)劃任務(wù),但它不會(huì)干擾任何當(dāng)前正在執(zhí)行的任務(wù)或操作。
在這個(gè)例子中,我們將看到 for 循環(huán)中的語(yǔ)句將繼續(xù)執(zhí)行,即使在遇到第一個(gè)“停止調(diào)用”語(yǔ)句后,即“i”等于 3。
現(xiàn)在我們將繼續(xù)下面給出的 purge() 方法的示例。
import java.util.*;
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
// run() method to carry out the action of the task
public void run() {
for(int i=1; i<= 10; i++) {
System.out.println("Keep on calling");
if(i >= 3) {
System.out.println("Stop calling");
// cancel method to cancel the execution
timer.cancel();
}
}
};
};
/*
* schedule() method to schedule the execution with start time
*/
timer.schedule(task, 5000, 5000);
}
}
輸出:
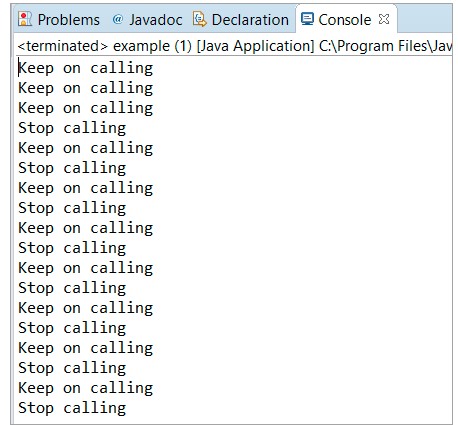
如果您比較為 cancel() 和 purge() 方法給出的示例,您會(huì)注意到在下面的 purge() 方法示例中,在 cancel() 方法之后放置了一個(gè) break 語(yǔ)句。這將允許控件在“i”變?yōu)?3 時(shí)立即退出循環(huán)。
現(xiàn)在我們已經(jīng)退出循環(huán),我們嘗試返回從隊(duì)列中刪除的任務(wù)數(shù)。為此,我們?cè)谝米兞康膸椭潞?jiǎn)單地調(diào)用了 purge 方法。
import java.util.*;
public class example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask task = new TimerTask() {
// run() method to carry out the action of the task
public void run() {
for(int i=1; i<= 10; i++) {
System.out.println("Keep on calling");
if(i >= 3) {
System.out.println("Stop calling");
// cancel method to cancel the execution
timer.cancel();
break;
}
}
// Purge after cancellation
System.out.println("Purge " + timer.purge());
};
};
/*
* schedule() method to schedule the execution with start time
*/
timer.schedule(task, 5000, 5000);
}
}
輸出:

以上就是關(guān)于“設(shè)置Java計(jì)時(shí)器的示例”介紹,大家如果想了解更多相關(guān)知識(shí),可以關(guān)注一下動(dòng)力節(jié)點(diǎn)的Java在線學(xué)習(xí),里面的課程內(nèi)容從入門到精通,細(xì)致全面,很適合小白學(xué)習(xí),希望對(duì)大家能夠有所幫助。
相關(guān)閱讀
 Java實(shí)驗(yàn)班
Java實(shí)驗(yàn)班
0基礎(chǔ) 0學(xué)費(fèi) 15天面授
 Java就業(yè)班
Java就業(yè)班
有基礎(chǔ) 直達(dá)就業(yè)
 Java夜校直播班
Java夜校直播班
業(yè)余時(shí)間 高薪轉(zhuǎn)行
 Java在職加薪班
Java在職加薪班
工作1~3年,加薪神器
 Java架構(gòu)師班
Java架構(gòu)師班
工作3~5年,晉升架構(gòu)
提交申請(qǐng)后,顧問(wèn)老師會(huì)電話與您溝通安排學(xué)習(xí)