更新時(shí)間:2019-08-16 11:34:46 來源:動(dòng)力節(jié)點(diǎn) 瀏覽2388次
最近有好多學(xué)員問小編Java對(duì)象序列化操作的問題,今天動(dòng)力節(jié)點(diǎn)java學(xué)院小編用實(shí)例講述Java對(duì)象序列化操作,希望看完此文后,對(duì)大家有幫助。
當(dāng)兩個(gè)進(jìn)程在進(jìn)行遠(yuǎn)程通信時(shí),彼此可以發(fā)送各種類型的數(shù)據(jù)。無(wú)論是何種類型的數(shù)據(jù),都會(huì)以二進(jìn)制序列的形式在網(wǎng)絡(luò)上傳送。發(fā)送方需要把這個(gè)Java對(duì)象轉(zhuǎn)換為字節(jié)序列,才能在網(wǎng)絡(luò)上傳送;接收方則需要把字節(jié)序列再恢復(fù)為Java對(duì)象。
只能將支持 java.io.Serializable 接口的對(duì)象寫入流中。每個(gè) serializable 對(duì)象的類都被編碼,編碼內(nèi)容包括類名和類簽名、對(duì)象的字段值和數(shù)組值,以及從初始對(duì)象中引用的其他所有對(duì)象的閉包。
概念
序列化:把Java對(duì)象轉(zhuǎn)換為字節(jié)序列的過程。
反序列化:把字節(jié)序列恢復(fù)為Java對(duì)象的過程。
用途
對(duì)象的序列化主要有兩種用途:
(1)把對(duì)象的字節(jié)序列永久地保存到硬盤上,通常存放在一個(gè)文件中;
(2)在網(wǎng)絡(luò)上傳送對(duì)象的字節(jié)序列。
對(duì)象序列化
序列化API
java.io.ObjectOutputStream代表對(duì)象輸出流,它的writeObject(Object obj)方法可對(duì)參數(shù)指定的obj對(duì)象進(jìn)行序列化,把得到的字節(jié)序列寫到一個(gè)目標(biāo)輸出流中。只有實(shí)現(xiàn)了Serializable和Externalizable接口的類的對(duì)象才能被序列化。
java.io.ObjectInputStream代表對(duì)象輸入流,它的readObject()方法從一個(gè)源輸入流中讀取字節(jié)序列,再把它們反序列化為一個(gè)對(duì)象,并將其返回。
代碼示例
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Date;
public class ObjectSaver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
/*其中的 D:\\objectFile.obj 表示存放序列化對(duì)象的文件*/
//序列化對(duì)象
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\objectFile.obj"));
Customer customer = new Customer("王麻子", 24);
out.writeObject("你好!"); //寫入字面值常量
out.writeObject(new Date()); //寫入匿名Date對(duì)象
out.writeObject(customer); //寫入customer對(duì)象
out.close();
//反序列化對(duì)象
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\objectFile.obj"));
System.out.println("obj1 " + (String) in.readObject()); //讀取字面值常量
System.out.println("obj2 " + (Date) in.readObject()); //讀取匿名Date對(duì)象
Customer obj3 = (Customer) in.readObject(); //讀取customer對(duì)象
System.out.println("obj3 " + obj3);
in.close();
}
}
class Customer implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
public Customer(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String toString() {
return "name=" + name + ", age=" + age;
}
}
執(zhí)行結(jié)果
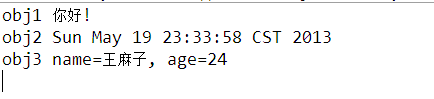
說明
讀取對(duì)象的順序與寫入時(shí)的順序要一致。
對(duì)象的默認(rèn)序列化機(jī)制寫入的內(nèi)容是:對(duì)象的類,類簽名,以及非瞬態(tài)和非靜態(tài)字段的值。
常見序列化操作
打印流
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("E:" + File.separator + "myFile" + File.separator + "test" + File.separator + "123.txt");
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
PrintStream printStream = new PrintStream(outputStream);
printStream.print(123);
printStream.println("hello");
printStream.println(12.5);
printStream.close();
}
}
鍵盤輸入讀取到程序中
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream in = System.in;
byte[] data = new byte[100];
System.out.println("輸入數(shù)據(jù):");
int read = in.read(data);
System.out.println(read);
System.out.println(new String(data,0,read));
}
}
掃碼流
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(new FileInputStream(new File("E:" + File.separator + "myFile" + File.separator + "test" + File.separator + "123.txt")));
scanner.useDelimiter("\n");
while (scanner.hasNext()){
String next = scanner.next();
System.out.println(next);
}
scanner.close();
}
}
scanner.useDelimiter("\n");表示以回車(換行)為定界符,回車間為一段掃碼的內(nèi)容。
掃描鍵盤輸入
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
注意:使用while判斷鍵盤輸入,程序可能會(huì)無(wú)法結(jié)束
對(duì)象序列化
序列化操作類:ObjectOutputStream,寫到文件中
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
A a = new A("hello", 123);
File file = new File("E:" + File.separator + "myFile" + File.separator + "test" + File.separator + "a.ser");
OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file);
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(outputStream);
objectOutputStream.writeObject(a);
objectOutputStream.close();
}
}
class A implements Serializable {
private String title;
private Integer number;
public A(String title, Integer number) {
this.title = title;
this.number = number;
}
public String getTitle() {
return title;
}
public void setTitle(String title) {
this.title = title;
}
public Integer getNumber() {
return number;
}
public void setNumber(Integer number) {
this.number = number;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "A{" +
"title='" + title + '\'' +
", number=" + number +
'}';
}
}
實(shí)體需要實(shí)現(xiàn)可序列化的接口implements Serializable,表示一種能力
反序列化操作類:ObjectInputStream,讀到程序里
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
File file = new File("E:" + File.separator + "myFile" + File.separator + "test" + File.separator + "a.ser");
InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream(file);
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(inputStream);
A a = (A) objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println(a);
}
}
transient關(guān)鍵字,實(shí)體的屬性使用該關(guān)鍵子,進(jìn)行序列化時(shí)該屬性值將不會(huì)被保存,反序列化的結(jié)果為,該屬性的值為該屬性類型的默認(rèn)值。
private String title;
private transient Integer number;
以上就是動(dòng)力節(jié)點(diǎn)java學(xué)院小編介紹的“Java對(duì)象序列化操作詳解”的內(nèi)容,希望對(duì)大家有幫助,更多精彩內(nèi)容請(qǐng)關(guān)注動(dòng)力節(jié)點(diǎn)java學(xué)院官網(wǎng),每天會(huì)有java最新內(nèi)容分享與你。
相關(guān)閱讀
 Java實(shí)驗(yàn)班
Java實(shí)驗(yàn)班
0基礎(chǔ) 0學(xué)費(fèi) 15天面授
 Java就業(yè)班
Java就業(yè)班
有基礎(chǔ) 直達(dá)就業(yè)
 Java夜校直播班
Java夜校直播班
業(yè)余時(shí)間 高薪轉(zhuǎn)行
 Java在職加薪班
Java在職加薪班
工作1~3年,加薪神器
 Java架構(gòu)師班
Java架構(gòu)師班
工作3~5年,晉升架構(gòu)
提交申請(qǐng)后,顧問老師會(huì)電話與您溝通安排學(xué)習(xí)